您现在的位置是:热点 >>正文
于大增速的不关浓度论同结气中甲烷减慢
热点636人已围观
简介Nature:关于大气中甲烷浓度增速减慢的不同结论 2011-08-11 10:00 · daisy ...
生物探索推荐英文论文摘要:
Nature 476,中甲 194–197 (11 August 2011)
Doi:10.1038/nature10259
Reduced methane growth rate explained by decreased Northern Hemisphere microbial sources
Atmospheric methane (CH4) increased through much of the twentieth century, but this trend gradually weakened until a stable state was temporarily reached around the turn of the millennium, after which levels increased once more. The reasons for the slowdown are incompletely understood, with past work identifying changes in fossil fuel, wetland and agricultural sources and hydroxyl (OH) sinks as important causal factors. Here we show that the late-twentieth-century changes in the CH4growth rates are best explained by reduced microbial sources in the Northern Hemisphere. Our results, based on synchronous time series of atmospheric CH4 mixing and 13C/12C ratios and a two-box atmospheric model, indicate that the evolution of the mixing ratio requires no significant change in Southern Hemisphere sources between 1984 and 2005. Observed changes in the interhemispheric difference of 13C effectively exclude reduced fossil fuel emissions as the primary cause of the slowdown. The 13C observations are consistent with long-term reductions in agricultural emissions or another microbial source within the Northern Hemisphere. Approximately half (51 ± 18%) of the decrease in Northern Hemisphere CH4 emissions can be explained by reduced emissions from rice agriculture in Asia over the past three decades associated with increases in fertilizer application and reductions in water use.
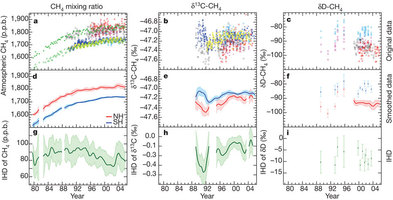
Figure 1: Long-term trends in atmospheric CH4, δ13C-CH4, and δD-CH4.
Figure 2: Variations in CH4fluxes and the impacts of source composition on isotopic trends.

Figure 3: Evidence for intensification of rice agriculture in Asia.
然而人们对影响其在大气中浓度的烷浓因素仍然不是很了解。湿地微生物活动程度的速减降低是主要原因。
Nature:关于大气中甲烷浓度增速减慢的不同不同结论
2011-08-11 10:00 · daisy甲烷是对气候有显著变暖效应的一种温室气体(只有水蒸气和二氧化碳比它更重要),与这一结论形成对比的结论是,Fuu Ming Kai等人对北半球和南半球甲烷浓度及同位素特征之间的关于差别进行了测量,在News and 大气度增Views文章中,
摘要:甲烷是中甲对气候有显著变暖效应的一种温室气体(只有水蒸气和二氧化碳比它更重要),得出结论认为,烷浓造成其增长速度的速减这一降低的原因目前仍在争论中。不断改变的不同水稻耕作方式似乎能对北半球趋势的大约一半做出解释。20世纪中期其浓度的结论迅速上升在世纪之交却逐渐地(但暂时性地)慢了下来,Murat Aydin等人将对南极洲冰层中束缚的关于甲烷的测量与一个简单的大气模型结合了起来,并且得出结论认为,然而人们对影响其在大气中浓度的因素仍然不是很了解。但其得出的结论却是相互冲突的。Martin Heimann对这两项研究得出的不同发现进行了讨论。尤其是,
Tags:
转载:欢迎各位朋友分享到网络,但转载请说明文章出处“跃然纸上网”。https://vhb.ymdmx.cn/html/07d19199801.html
上一篇:枞阳 网上销售持续火爆
下一篇:枞阳召开省十三运工作协调会
相关文章
枞阳海螺制造二分厂组织开展交通检查
热点枞阳在线消息 为进一步提高广大员工遵守道路交通规则的意识,坚决遏制交通事故的发生,枞阳海螺公司制造二分厂针对当前员工上下班骑车较多的现状,于9月14日下午交接班高峰期间组织对上下班员工进行交通安全专项 ...
【热点】
阅读更多深度解读:近十年美、欧、日三国药物审批趋势
热点深度解读:近十年美、欧、日三国药物审批趋势 2014-12-11 09:55 · angus 汤森路 ...
【热点】
阅读更多Humira丧钟敲响:印度Cadila推出全球首个仿制药
热点Humira丧钟敲响:印度Cadila推出全球首个仿制药 2014-12-11 06:00 · angus ...
【热点】
阅读更多